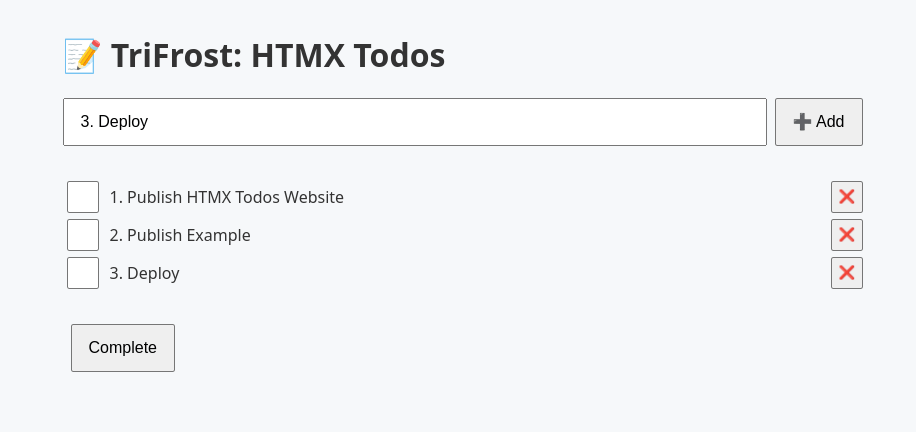
TriFrost + HTMX Todo App
This example showcases a fully interactive, stateful todo application using TriFrost HTMX.
How It Works
This app is entirely server-rendered using TriFrost. Routing, HTML generation, and persistent state are all handled within a single index.tsx entrypoint. Todos are stored durably using a DurableObjectCache — so no database setup is needed. TriFrost's built-in JSX and CSS support means UI fragments are returned directly from route handlers.
On the frontend, HTMX listens for form submissions and button clicks, then sends HTTP requests via attributes like hx-post and hx-delete. The server responds with fragment HTML — e.g. just the updated todo list — and HTMX swaps it seamlessly into the page.
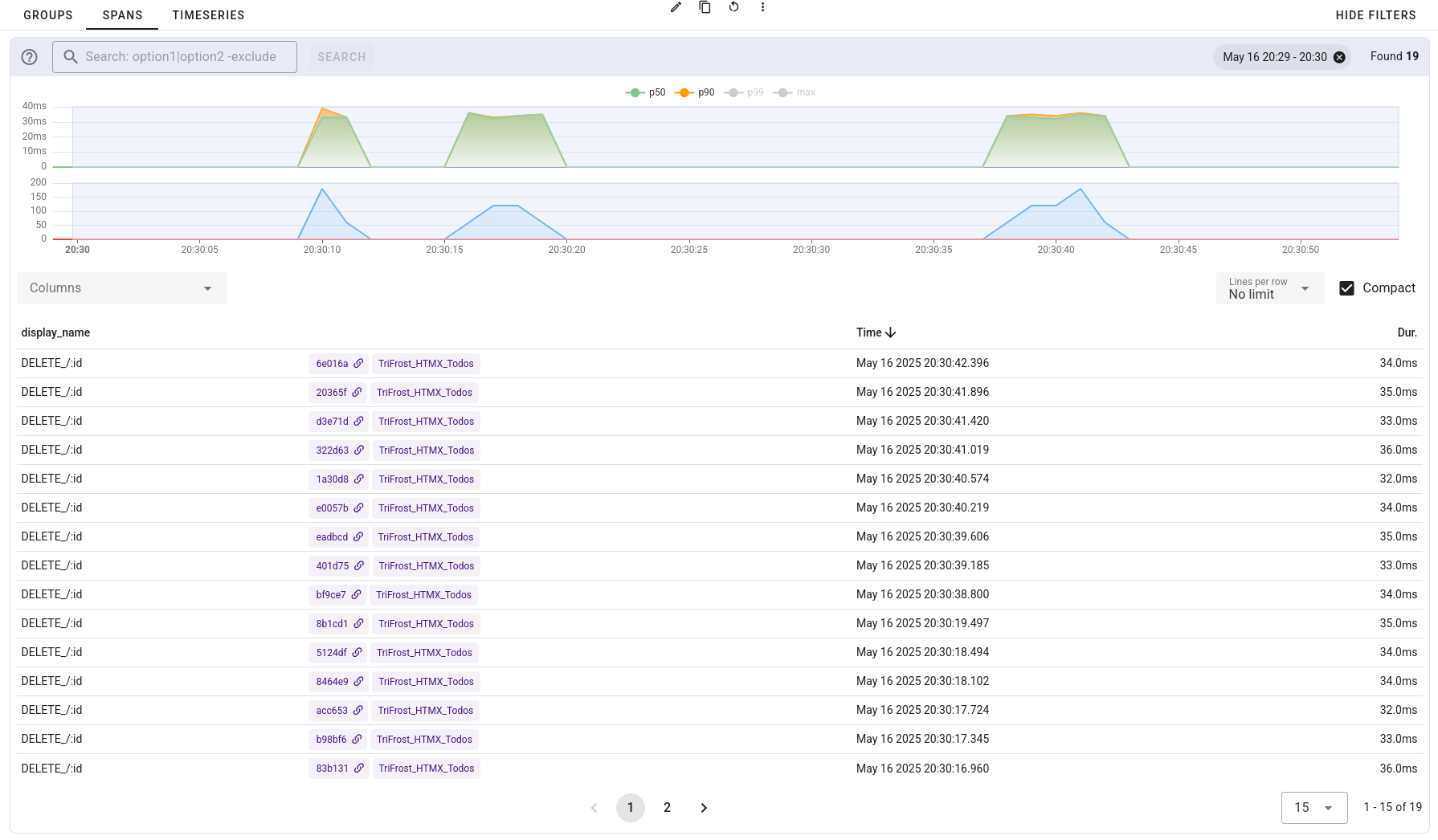
🧪 Observability is baked in. Every request is traced using OpenTelemetry and exported to UpTrace. App metadata like name and version are included automatically in every span, with no boilerplate required. You can inspect the performance and behavior of each route in full detail.
Project Structure
my-todos/
├─ public/
│ ├─ favicon.ico
│ └─ ...
├─ src/
│ ├─ components/
│ │ ├─ Footer.tsx
│ │ ├─ Layout.tsx
│ │ └─ Todos.tsx
│ ├─ index.tsx
│ └─ css.ts
│ └─ types.ts
├─ wrangler.tomlLogic
The main app logic lives in src/index.tsx, where TriFrost routes, renders, and manages state for the entire todo application using a Durable Object–backed cache.
The client option with our css instance ensures TriFrost Atomic (0.36+) automounts our css root to /__atomics__/client.css, ensuring no repeat global styles but only page-specific styles get inlined.
// src/index.tsx
import {App, DurableObjectCache, OtelHttpExporter} from '@trifrost/core';
import {Layout} from './components/Layout';
import {TodoForm, TodoList, type Todo} from './components/Todos';
import {type Env} from './types';
import {css} from './css';
export {TriFrostDurableObject} from '@trifrost/core';
const app = await new App<Env>({
client: {css},
cache: ({env}) => new DurableObjectCache({store: env.MAIN_DURABLE}),
tracing: {exporters: ({env}) => [
new OtelHttpExporter({
logEndpoint: 'https://otlp.uptrace.dev/v1/logs',
spanEndpoint: 'https://otlp.uptrace.dev/v1/traces',
headers: {'uptrace-dsn': env.UPTRACE_DSN},
}),
]},
})
.get('/', async ctx => {
const todos = await ctx.cache.get<Todo[]>('todos') || [];
return ctx.html(<Layout>
<main className={css({
width: '100%',
maxWidth: '50rem',
flexGrow: '1',
})}>
<h1 style={css.mix('title')}>📝 TriFrost: HTMX Todos</h1>
<TodoForm />
<TodoList todos={todos} />
</main>
</Layout>);
})
.post('/', async ctx => {
let todos = await ctx.cache.get<Todo[]>('todos') || [];
const text = String((ctx.body as {text:string}).text || '');
if (todos.findIndex(el => el.text === text) < 0) {
todos.push({id: crypto.randomUUID(), text});
todos = todos.slice(0, 50);
await ctx.cache.set('todos', todos);
}
return ctx.html(<TodoList todos={todos} />);
})
.del('/:id', async ctx => {
let todos = await ctx.cache.get<Todo[]>('todos') || [];
todos = todos.filter(t => t.id !== ctx.state.id);
await ctx.cache.set('todos', todos);
return ctx.html(<TodoList todos={todos} />);
})
.post('/complete', async ctx => {
const todos = await ctx.cache.get<Todo[]>('todos') || [];
const {done} = ctx.body as {done?: string|string[]};
const to_complete = new Set(typeof done === 'string' ? [done] : Array.isArray(done) ? done : []);
if (to_complete.size) {
for (const todo of todos) {
if (to_complete.has(todo.id)) todo.completed = true;
}
await ctx.cache.set('todos', todos);
}
return ctx.html(<TodoList todos={todos} />);
})
.boot();
export default app;Components
All UI elements like the todo form and todo list live in self-contained components under src/components/. Each component renders server-side JSX and uses HTMX attributes to hook into behavior as well as using the TriFrost css instance for styling.
// src/components/Todos.tsx
import {css} from "../css";
export type Todo = {
id:string;
text:string;
completed?:boolean;
};
export function TodoForm () {
return (<form
className={css.use('form', {gap: css.$v.space_m})}
hx-post="/"
hx-trigger="submit"
hx-target="#todo-list"
hx-swap="outerHTML"
>
<input
type="text"
name="text"
required
placeholder="Add new todo..."
className={css.use('form_el', {flexGrow: 1})} />
<button
type="submit"
className={css.use('button', 'button_l')}>Add</button>
</form>);
}
export function TodoList (props:{children?:any; todos:Todo[]}) {
const todos = props.todos || [];
const hasTodos = todos.length > 0;
return (<section id="todo-list">
{!hasTodos && <p className={css({
textAlign: 'center',
padding: css.$v.space_l,
backgroundColor: css.$t.empty_bg,
borderRadius: css.$v.radius,
color: css.$t.empty_fg,
})}><em>No todos yet</em></p>}
{hasTodos && (<form
className={css.use('f', 'fv', 'form', {alignItems: 'flex-start'})}
hx-post="/complete"
hx-trigger="submit"
hx-target="#todo-list"
hx-swap="outerHTML"
>
<ul style={{width: '100%'}}>
{todos.map(t => <li
key={t.id}
id={`todo-${t.id}`}
className={css.use('f', 'fa_c', {
gap: css.$v.space_s,
width: '100%',
maxWidth: '100%',
})}>
<input
type="checkbox"
name="done"
value={t.id}
disabled={t.completed}
className={css.use('form_icon')} />
<span className={css.use({
flexGrow: 1,
overflow: 'hidden',
textOverflow: 'ellipsis',
textDecoration: t.completed ? 'line-through' : 'none'
})}>{t.text}</span>
<button
type="button"
className={css.use('button', 'button_s')}
hx-delete={`/${t.id}`}
hx-target="#todo-list"
hx-swap="outerHTML"
>Remove</button>
</li>)}
</ul>
<button
type="submit"
className={css.use('button', 'button_l', {marginTop: css.$v.space_m})}
>Complete</button>
</form>)}
</section>);
}Layout
The layout component wraps full-page responses, injecting meta tags, the HTMX script, and optional UI elements like footers, ....
// src/components/Layout.tsx
import {css} from '../css';
export function Layout (props:{children:any}) {
return (<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>TriFrost & HTMX | Todos</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<meta name="description" content="Manage your todos with TriFrost and HTMX" />
<script src="https://unpkg.com/htmx.org"></script>
</head>
<body className={css.use(...)}>
{props.children}
</body>
</html>);
}Styling
Instead of a single prebuilt global css file which gets included everywhere (and of which probably 10% is used per page) the css module automatically collects what is used on the page's components and injects it as inline styling.
It does just a bit more than that, in this particular case we're also injecting a css reset as well as defining reusable definitions and theme/global variables..
Important Notes:
- definitions are not included in the css if not used. They form your backbone to centralize reusable pieces of styling without bloating the page if not used, they get merged in with client styles by using
css.useandcss.mix. - Since TriFrost 0.36 Atomic, global styles such as the css reset and theme/global variables get bundled in a file and mounted at
__atomics__/client.cssif you pass yourcssinstance as part of the client options on App. The system takes care of adding the link automatically to your output HTML.
// src/css.ts
import {createCss} from "@trifrost/core";
export const css = createCss({
reset: true,
var: {
space_s: '.5rem',
space_m: '1rem',
space_l: '2rem',
radius: '.4rem',
},
theme: {
body_bg: '#f6f8fa',
body_fg: '#333333',
empty_bg: '#ededed',
empty_fg: '#666',
},
definitions: mod => ({
f: () => ({display: 'flex'}),
fv: () => ({flexDirection: 'column'}),
fh: () => ({flexDirection: 'row'}),
fa_c: () => ({alignItems: 'center'}),
title: () => ({
fontSize: '1.8rem',
fontWeight: 600,
}),
form: () => ({
display: 'flex',
margin: `${mod.$v.space_m} 0`,
}),
button: () => ({
appearance: 'none',
backgroundColor: 'black',
color: 'white',
border: 'none',
cursor: 'pointer',
textAlign: 'center',
flexShrink: 0,
borderRadius: mod.$v.radius,
fontWeight: 600,
[mod.hover]: {
backgroundColor: '#333',
},
}),
button_l: () => ({
lineHeight: '3rem',
padding: `0 ${mod.$v.space_m}`,
fontSize: '1rem',
}),
button_s: () => ({
lineHeight: '2rem',
padding: `0 ${mod.$v.space_s}`,
fontSize: '.8rem',
}),
form_el: () => ({
fontSize: '1rem',
height: '3rem',
padding: `0 ${mod.$v.space_m}`,
borderRadius: mod.$v.radius,
}),
form_icon: () => ({
fontSize: '1rem',
height: '2rem',
width: '2rem',
display: 'inline-block',
flexShrink: '0',
}),
})
});Environment
All environment bindings expected by the app — such as the durable object, asset fetcher, and optional Uptrace DSN — are defined in src/types.ts for type safety and clarity.
This exported Env type is also used as a generic for the App, this generic ensures each of the routes (as well as the app configuration itself) knows the environment.
Pro-tip: You can access the environment through
ctx.envin any route handler.
// src/types.ts
export type Env = {
ASSETS: Fetcher;
MAIN_DURABLE: DurableObjectNamespace;
UPTRACE_DSN: string; /* DSN from uptrace */
};Cloudflare
The wrangler.toml config defines how your app runs on Cloudflare — including bindings for assets and durable objects, compatibility flags, and deployment metadata.
Note: If you're using Otel tracing ensure to add
TRIFROST_NAMEand (optionally)TRIFROST_VERSIONto your environment variables. These get picked up by TriFrost to automatically enrich your trace spans. If not set we will default totrifrostand1.0.0if not set.
// wrangler.toml
name = "trifrost_htmx_todos"
main = "src/index.tsx"
compatibility_date = "2025-05-08"
compatibility_flags = ["nodejs_compat"]
[vars]
TRIFROST_NAME = "TriFrost_HTMX_Todos"
TRIFROST_VERSION = "1.0.0"
[assets]
directory = "./public/"
binding = "ASSETS"
[[durable_objects.bindings]]
name = "MAIN_DURABLE" # This is the name of our durable object (see src/types.ts)
class_name = "TriFrostDurableObject" # This is the class exported from src/index.ts
[[migrations]]
tag = "v1"
new_sqlite_classes = ["TriFrostDurableObject"] # This is a requirement by CloudflareResources
- HTMX: Add AJAX, WebSockets, and more to HTML using attributes.
- CloudFlare Durable Objects: Low-latency stateful storage at the edge.
- UpTrace: OTel-powered observability backend used in this example.
- HTML Forms (MDN): Useful refresher on native forms.